Understanding Acupressure:
A Path to Natural Healing
Acupressure, an ancient healing practice rooted in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), is a holistic technique that involves applying pressure to specific points on the body to alleviate pain, reduce stress, and promote overall well-being. Often referred to as the “massage version” of acupuncture, acupressure is non-invasive and does not require needles, making it an accessible and popular form of therapy worldwide.
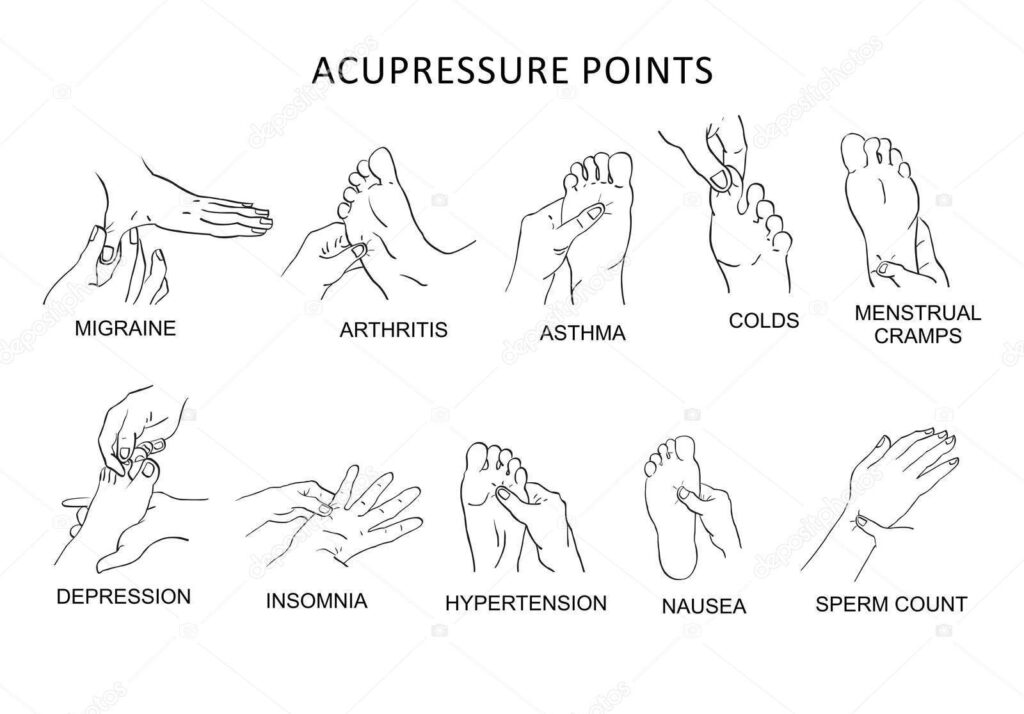
The Philosophy Behind Acupressure
Acupressure is based on the concept of “Qi” (pronounced “chi”), the vital energy that flows through the body’s meridians, or energy pathways. According to TCM, blockages or imbalances in this energy flow can lead to physical and emotional ailments. By stimulating specific acupressure points along these meridians, practitioners aim to restore balance and harmony to the body, enabling its natural healing mechanisms.
Key Acupressure Points and Their Benefits
LI4 (Hegu) – Located on the hand
- Benefits: Relieves headaches, stress, and facial pain.
- How to Find: The soft area between the thumb and index finger.
PC6 (Neiguan) – Found on the wrist
- Benefits: Eases nausea, motion sickness, and anxiety.
- How to Find: Three finger-widths below the wrist on the inner forearm.
SP6 (Sanyinjiao) – Situated on the lower leg
- Benefits: Improves digestion, alleviates menstrual cramps, and reduces insomnia.
- How to Find: Four finger-widths above the inner ankle bone, near the shinbone.
GV20 (Baihui) – Located on the crown of the head
- Benefits: Calms the mind, reduces stress, and improves focus.
- How to Find: The highest point on the head when ears are level.
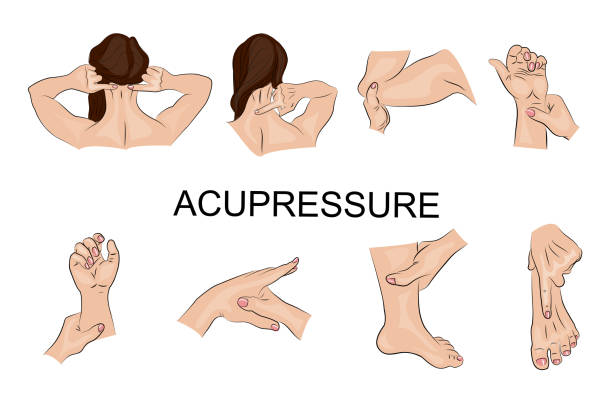


Benefits of Acupressure
Acupressure offers a multitude of physical and emotional health benefits, including:
- Pain Relief: Effective for conditions such as back pain, migraines, and arthritis.
- Stress Reduction: Promotes relaxation by lowering cortisol levels.
- Improved Circulation: Stimulates blood flow and oxygen supply.
- Enhanced Digestion: Alleviates bloating and other digestive issues.
- Better Sleep: Helps treat insomnia by calming the nervous system.
Our Guarantee

How to Practice Acupressure
- Find the Right Points: Use reliable diagrams or consult a professional.
- Apply Gentle Pressure: Use your fingers, thumb, or a rounded object.
- Be Consistent: Practice regularly for noticeable results.
- Listen to Your Body: Discontinue if you feel discomfort or pain.
Who Can Benefit?
Acupressure is generally safe for people of all ages. However, individuals with certain conditions, such as pregnancy, fractures, or severe illnesses, should consult a healthcare provider before starting acupressure therapy.
Acupressure is a simple yet powerful tool that harnesses the body’s natural ability to heal. By integrating this ancient practice into daily life, individuals can experience improved physical health and emotional balance. Whether practiced independently or alongside other treatments, acupressure serves as a bridge between modern science and traditional wisdom.
